Why study the computer? Here's a short video on why people study the computer:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1o0oA3fa2ws
As we see, the innovation of computers and its softwares has just began. The technologies and scientific breakthroughs in this world is rapidly improving, and computers are not to be left behind.
IT AND YOUR LIFE: THE FUTURE NOW
Information Technology: any technology that helps to produce, manipulate, store, communicate, and/or disseminate information.
So how is IT being used in the society?
1.) Education
2.) Healthcare

3.) Leisure
4.) Much other more
- Government
- Job searching
- Banks
- Hotels
This video summarizes what IT is doing for our society:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2E46iFQgV1M
IT IS ALL PERVASIVE
1.) Cellphone
- First call in 1973
- Today's phones are able to connect to internet, take and send pictures, obtain news, send and receive text.

2.) Email
- Introduced in 1981
- Fastest-growing technology
3.) Internet, World Wide Web, and Cyberspace
a.) Cyberspace
- encompasses Internet and World Wide Web
- wired and wireless communications world
b.) Internet
- worldwide computer network that links smaller networks
- developed to share data
c.) World Wide Web
- multimedia part of internet
- interconnected system of servers
FIVE TYPES OF COMPUTERS
1.) Supercomputers
- thousands of processors
- multi-user systems
2.) Mainframes
- water or air-cooled computers
- used mainly in large businesses and organizations
3.) Workstations














.gif)







- used mainly for computer-aided design
- used for designing cars, drugs, special effects

4.) Microcomputers
- computers we most are familiar with
- includes desktop, notebooks, netbooks, tablets, e-readers, etc.
5.) Servers
- central computer connected to other computers on a client-server network
- hold data and programs for clients to access
BASIC COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER


CHAPTER 2: THE INTERNET & THE WORLD WIDE WEB EXPLORING CYBERSPACE
A brief history of the internet:
Some terms you need to know
1.) Bandwidth- data that can be sent through in a given amount of time..
2.) Baseband- slow type of connection allowing only one signal at a time.
3.) Broadband- high-speed connection allowing several signals
*Connections to the internet can be wired or wireless
Connections like dial- up, need a telephone modem which would be wired to the computer. However, wireless connections also exist like the satellite connection.
How does the internet work?
The internet consists of hundreds of thousands of smaller networks. These networks would be defined as the client-server network.
The client is the computer requesting the data or services while the server is the one supplying the data or services requested of it.
POP, IXPs, and Backbone
In order for clients to be able to connect to the internet, three things are usually required. First is the Point of Presence or POP. It is defined as a collection of modems and equipments in a local area and also a local gateway to an ISP's network. Second is the Internet Exchange Point or IXP. It is where ISPs exchange internet traffic of their networks and also a point on the Internet where several connections come together. Last is the Internet Backbone. These are the high-speed, high capacity data transmission lines.

IP Addresses
IP addresses are four sets of numbers between 0 to 255 that provide addresses and identify a device. IP addresses are classified into two: Dyanamic IP which change with every use and Static IP that doesn't change.
THE WORLD WIDE WEB
Web and internet are not the same. Web is multimedia based, but the internet is not. The Web consists of these parts:
1.) Browsers- softwares for web surfing like google chrome, mozilla firefox, safari, etc.
2.) Website- location on a particular computer and has unique address
3.) Web Page- document of the page.

4.) Uniform Resource Locator (URL)- a website's unique address
ex. https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=history+of+the+internet
Search Services and Search Engines
Organizations that maintain databases accessible. Some of the most popular search services are Google, Yahoo, and Bing. Databases of search engines are compiled using software programs called spiders. There are four web search tools. Mainly Individual search engines, subject directories, metasearch engines, and specialized search engines.
1.) Individual search engines- compile their own databases on the web
ex. google, yahoo
2.) Subject Directories- created by human editors, not electronic spiders
ex. Google Directory, Yahoo! Directory
3.) Metasearch Engines- search several search engines simultaneously
ex. Mamma, Dogpile
4.) Specialized Search Engines- specialized subject matter
ex. Census, Health survey, Career.com
Email and Other Internet Communication
Email is defined into two parts: Outgoing mail and Incoming mail. Outgoing mail being the mail that is being sent and Incoming mail being the email sent to the computer.
Two ways to send and receive mail
1.) Email Program- software that allows email to be sent or received.
ex. Microsoft Outlook, Apple Mail
2.) Web-based Email- send or receive mail through interaction with a browser and a website
ex. Yahoo mail, Google mail
Netiquette
We as people should act accordingly in the web. Even more so because the net has a lot of users. These are some of the netiquettes that should be followed.
- Avoid flaming
- Dont shout
- Be careful with jokes
- Don't send huge file attachments
The Intrusive Internet
Malware- software intended to do unwanted actions on a computer system
Snooping- email is not private
ex. corporate management has right to view employees' email
Spam- electronic junk mail
*report spammers to www.abuse.net or www.spamhaus.org
Spoofing- using of fake email or sender name
Phishing- fake websites enticing people to share personal data

Cookies- make visiting websites more convenient and faster, however, can also be used to gather information without consent.
Spyware- softwares secretly installed on the computer via web
CHAPTER 3: SOFTWARE TOOLS for PRODUCTIVITY & CREATIVITY
This video will show the difference between Application Software and System Software
A System Software has three basic components
- Operating System- principal component of system software
- Device Drivers- help the computer control peripheral devices
- Utility Programs- used to support, enhance, or expand existing programs
So what is an Operating System?
The Operating System is used to manage basic computer operations, so without it, we wouldn't find using a computer fun. Which also means that every computer must have an Operating System to run other programs. Some OS functions include booting, CPU management, file management, task management, and security management.
1.) Booting- loading an OS into a computer's main memory
- Cold Boot- turn the computer on
- Warm Boot- restart the computer (computer should be already on).
- Boot disk- use a diskette or CD to launch OS
2.) CPU Management-
- Supervisor- software that manages the CPU.
- Memory Management- prevents programs and data from overlapping
3.) File Management- finds files using their pathname
4.) Task Management- manages tasks the computer is performing
5.) Security Management- most commonly seen as the username and password.
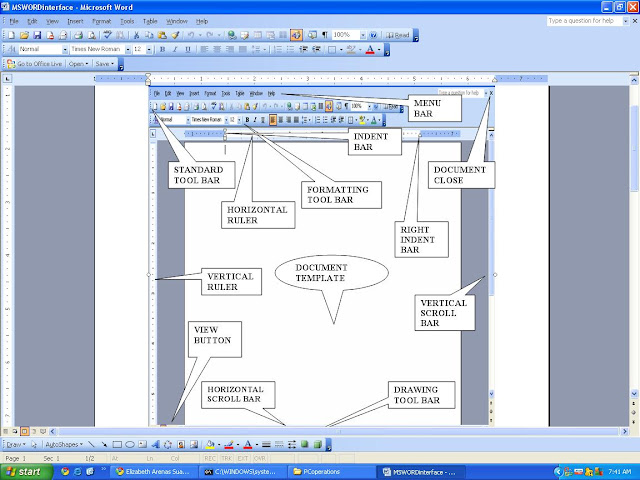
Common Features of the User Interface
User Interface- display screen used to interact with computer, using keyboard or mouse.
Parts of the keyboard:

Graphical User Interface (GUI)- allows the selection of icons and commands from menus
Common Operating Systems- processor model and OS the computer system is based.
FIVE LEGAL TYPES OF APPLICATION SOFTWARE
1. Commercial Software- offered for sale, different versions which have upgrades are available
2. Public- domain Software- Free to the public, not copyrighted
.gif)
3. Shareware- downloaded for free, but should pay if want to use

4. Freeware- copyrighted but free

5. Rentalware- copyrighted, lease for a fee

TYPES OF APPLICATION SOFTWARE AND SYSTEM SOFTWARE

WORD PROCESSING SOFTWARES
Word processing is defined as the usage of computers to create, edit, format , print, and store text. One of the best known Word Processing software is the Microsoft Word. This type of software also allows the editing of the text.

Spreadsheet programs are used to create tables and input data horizontally or vertically called cells. A known Spreadsheet program would be Microsoft Excel.

Database Software
A Database is defined as a structured collection of interrelated files in a computer system. One known database would be Microsoft Access.

Presentation Graphic Software
This type of software uses graphics, animations, and data in making a visual presentation. One type of this software would be Microsoft Powerpoint.

Midterms
THE INTERNET AND THE WORLD WIDE WEB
The Internet could be your worst enemy or your best friend. We may choose to spend most of our time in leisure or we could engross ourselves learning what the Internet has to offer.
Internet, or International Network, requires three things: an access point, such as personal computers, a means of connection, like telephone wire, and an ISP or Internet Service Provider. This video could help you understand how the internet works.
THE INTERNET AND THE WORLD WIDE WEB
The Internet could be your worst enemy or your best friend. We may choose to spend most of our time in leisure or we could engross ourselves learning what the Internet has to offer.
Internet, or International Network, requires three things: an access point, such as personal computers, a means of connection, like telephone wire, and an ISP or Internet Service Provider. This video could help you understand how the internet works.
CONNECTING TO THE INTERNET
Of course, one factor of the internet we wish to have really fast is speed. One element that determines speed is the bandwidth. It is also known as how much data-text, voice, video, and so on-can be sent through a communications channel in a given amount of time. There are two types of bandwidth namely narrowband or low bandwidth connection and broadband.
Examples of broadband include:


And examples of narrowband include:

Also, there are some ways to connect to the internet without cables or wires. Some of these include: satellite wireless connection, wi-fi, 3G,4G.
SO WHO OWNS THE INTERNET?
Basically, no one owns the internet, but standards are made by organizations like ISOC or Internet Society and ICANN which stands for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers.
THE WORLD WIDE WEB- multimedia of the internet.
Before entering this class, I always thought that internet and world wide web are the same thing but there's a key difference. The world wide web is the medium in which we are able to see text, watch videos, listen to audio, and many more.
In order for us to use the World Wide Web we should have a browser. It is a software that enables you to go to different websites and web pages
COMMUNICATIONS , NETWORKS, and SAFEGUARDS
The beauty of our technology today is that is has become better. Before, computing devices and communication devices were two completely independent things, However, now, we have what we call digital convergence. There are signals the computer uses to communicate. A computer converts analogue signals to digital signal; a signal in which a computer understands. Digital signals use a binary system, which consist of only two digits, 0 and 1.

Since analog signals are signals that are continuous and are like real-life waveforms which the computer cannot understand. It has to translate to a signal it can understand which is the digital signal.
NETWORKS
Of course, one factor of the internet we wish to have really fast is speed. One element that determines speed is the bandwidth. It is also known as how much data-text, voice, video, and so on-can be sent through a communications channel in a given amount of time. There are two types of bandwidth namely narrowband or low bandwidth connection and broadband.
Examples of broadband include:


And examples of narrowband include:

Also, there are some ways to connect to the internet without cables or wires. Some of these include: satellite wireless connection, wi-fi, 3G,4G.
SO WHO OWNS THE INTERNET?
Basically, no one owns the internet, but standards are made by organizations like ISOC or Internet Society and ICANN which stands for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers.
THE WORLD WIDE WEB- multimedia of the internet.
Before entering this class, I always thought that internet and world wide web are the same thing but there's a key difference. The world wide web is the medium in which we are able to see text, watch videos, listen to audio, and many more.
In order for us to use the World Wide Web we should have a browser. It is a software that enables you to go to different websites and web pages
COMMUNICATIONS , NETWORKS, and SAFEGUARDS
The beauty of our technology today is that is has become better. Before, computing devices and communication devices were two completely independent things, However, now, we have what we call digital convergence. There are signals the computer uses to communicate. A computer converts analogue signals to digital signal; a signal in which a computer understands. Digital signals use a binary system, which consist of only two digits, 0 and 1.

Since analog signals are signals that are continuous and are like real-life waveforms which the computer cannot understand. It has to translate to a signal it can understand which is the digital signal.
NETWORKS
